|
III Multi functional theater
1. Frame stage multi functional theater
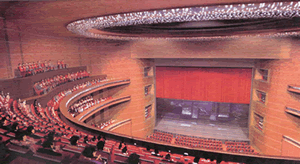
1)The auditorium hall
5 Stage
2. Open stage multi functional theater
IV Art Performance Center
The Author Introduction
I General
A theater has many complicated building types. To build an efficient and
successful theater both for the audience and performers, it requires a
solid understanding of the theater components and the relationship among
them.
1. Type of theaters
The main function of the building of performance art is for people to
watch performance. There are different buildings for different types of
performance in order to acquire the best results. There are five basic
modern building types of performance art:
Drama & opera theater: for drama and opera performances
Concert hall: for music performances
Singing & dancing theater: for opera, ballet, singing & dancing
drama performances
Multi functional theater: for multi-types of performances, including frame-stage
multi-function theater and black box multi-function theater
Performance center: a performance building complex include all above components.
Different types of performance building have different function requirements.
The primary task is to make the content and the type of the performance
art clear.
2. The function zone of the theater
Although the auditorium types vary a lot, from two or three hundred to
two or three thousand, the basic function components are the same, all
including the following parts:
The relaxing hall: A place for people to relax, socially communicate,
with a ticket office and exhibition function etc.
The auditorium hall: The place where people watch the performance, including
the orchestra pit and the stage: a place for the performance and rehearsal
Back stage: A place to provide the preparation and service for the performance,
which includes three parts: the actor/actress room, performance equipment
room and its transportation system plus on office room
The affiliated room: It includes the general and specialized electrical
facility room and car park equipment, which assure the above parts to
operate successfully
Among the above function zone, the relaxing hall and the auditorium hall
are the public activity zones, and the orchestra pit. The stage and the
back of the stage are the performers’ zones. The circulation of these
two parts should be separated, independent and not disturbing each other.
The electrical facility room should be separated from these two parts.
3. How the operation method influences the theater design
In the architectural design of a theater, the architect should realize,
how the operating method influences the design proposal.
For a theater with its own drama group, it should have more comprehensive
back stage facilities and meet the requirement of producing and storage
of large quantities of the drama settings, stage props and dresses. It
should provide permanent working rooms for all performers and managers
of the group. For a theater without its own drama group, which only serves
traveling groups, there is no need for big producing and storage space
of drama settings, stage props and dresses. The office room can be simpler.
The full consideration should be given to the transportation convenience
and the flexibility of the performance equipment.
For a commercial theater which aims at profit, the high ratio of the investment
and the profit is the target. So the auditorium hall should be enlarged
and the rest part should be reduced as much as possible, which assures
the performance’s effectiveness. For a non-profit purpose theater, the
area of function zone can be distributed according to the owner’s investment
and requirement.
4. The key points of the theater design procedure
The complexity of the theater building makes it impossible for most clients
and architects to be familiar with all details of the theater’s function,
so the following specialists must be involved:
Theater consultant: They should join in from the beginning of making design
proposal, assisting to decide the style and the main size of the theater,
the form and the main dimension of the stage. The technical requirement
details, including the detail dimension of all parts of the stage, the
application method of the stage mechanical equipment, has to be provided
during schematic drawing phase, consultation about the detail design,
to assure the function, has to be provided during the working drawing
phase.
Acoustic consultant: Acoustic design is very important in theater design.
It includes two main parts: the acoustic study of the auditorium hall
and the noise control. The acoustic consultant should get involved from
the schematic design period to assure, that there will be no acoustic
weakness inborn. Acoustic design should be carried out together with the
design of schematic drawing and working drawing, until the test of using
is finished.
Stage mechanicals designer: Stage mechanicals include the movable parts
above and below the stage and the hanging system above the stage. It should
be designed and coordinated together with the working drawings of the
construction design. The architect should coordinate with the mechanical
and electrical engineers during the early stages, due to their close relationship.
The architect, as the host, must coordinate with structure engineers,
facility engineers and electrical engineers.
Performance lighting, hi-fi and control system designers: performance
lighting, electrical sound and control system, are all closely connected
with the construction design, and should be designed together.
User (operator): if the owner and the user (operator) are different, the
architect should listen to the user (operator) as well to make the theater
more practical. The best way is to let the operator get involved from
the beginning.
5. Design specification
The main theater specifications used in mainland China are:
<The architectural design specification for theaters>
<The general principle of civil architectural design>
<The fire resistant specification of building design>
<The fire resistant specification of building interior renovation>
<The design specification of urban roads and building for disabled>
II The component of performance buildings
(for first three types)
As the drama & the opera, the singing & dancing theater, and the
concert hall have some requirements in common, they are described together
here.
1. The relaxing hall
The relaxing hall is the area where the audience can wait and relax. It
includes the public foyer and VIP lounge.
1) The public foyer
The public foyer is a larger space, where the audience can wait and relax.
It includes the front (main) vestibule and the side vestibule. The front
(main) vestibule is facing the auditorium hall and the sides ones are
on both sides of the auditorium hall. These two have no difference in
importance and size. It can be designed according to the architectural
form and site conditions.
For the function of the public foyer, facilities like dress store, shop,
toilet, and telephone are needed. The ticket office of the theater can
be arranged independently or as a part of the front vestibule, which is
convenient for walking in and out. The tea bar with chairs can be installed
in the foyer(There are only high coffee table without chairs and few high
stools by the bar counter in western theaters), smoking area/room is better
located at the end of the foyer. In some high standard theater there can
be a waiting area for late people, with closed circuit television viewing
the performance circumstances inside the auditorium hall. A small exhibition
can be held in the foyer, while larger ceremonies can be held in bigger
and grander foyer. There should be a general control room for all electricity
switches and a restroom for the service people, which also serves as cleaning
and store room.
For emergency issue, facilities like shop, store etc., should not block
the easy circulation line of the audience. The width of the emergency
door of the foyer should not be less than the one of the auditorium hall.
The ground square outside the emergency door should not be used as a car
park.
There should be a non-blocked way to the toilet for the disabled in the
public foyer. The toilet for the disables should be close to the seats
for disables in the auditorium hall.
For noise control issues, besides the sound absorbing arrangement for
the grand space and the sound control brake, the source of the noise,
which is difficult to control, should be noticed(the toilet and the lift
well). They should not be placed close to the auditorium hall. The toilet
should not be placed under the raised auditorium seats directly. In case
this cannot be avoided, low frequency isolation arrangement must be installed.
2) VIP lounge
VIP lounge is a space for VIP guest to wait and rest. The circulation
of VIP guest should be separated from the one of common audience, with
its own entrance and exit on a quiet corner of the building. The VIP lounge
can be connected to the VIP box or lies at an isolated location and connected
to the entrance via a special access.
There are special toilets and service rooms, or even a bar counter, for
VIP lounge.
There is a special car park for VIP guest at the entrance / exit.
2. The auditorium hall
The auditorium hall design is a very complicated design work including
the comprehensive performances and watching styles, interior design, auditorium
seats design, architectural acoustic design, performance lighting and
hi-fi design and the control room arrangement etc.
1) The performance watching styles
The watching style, the relationship between the auditorium seats and
the stage, should be defined according to the performance content first.
The next step is to design the layout plan and the sections.
a. Opera & drama house
The contemporary opera & drama has various styles, so the requirements
for performance watching styles of the theater vary accordingly. The basic
watching styles include traditional frame stage and modern open stage.
The open stage includes ended stage, extended stage, centered stage (island
stage), revolving stage and semi-revolving stage. Most of them in China
are frame stage style, only few theaters have raised orchestra pit as
the extended stage with low utilization ratio. Ended stage, centered stage,
revolving stage and semi-revolving stage mainly exist in temporary theaters.
The auditorium hall should assure the audience can feel the exquisite
emotion and sound of performers, so the auditorium volume is better not
to exceed 1200 seats.
b. Singing & dancing theater
Although opera, singing & dancing performance vary a lot, the basic
performances are carried out in the traditional frame stages. Most of
the performance content of singing & dancing have violent sound and
actions, so the restriction for sound and vision are looser. Besides,
the costs of these performances are quite high, and the theater sizes
are quite large in general. It will be difficult to solve natural sound
and vision problems if the audience seats exceeding 2000.
c. Concert halls
The two watching styles of the concert hall are the ended type and the
centered type. The ended type can be used for variety of sizes of concert
halls, while the centered type mainly appears in larger size concert halls.
Nowadays many large shoe-box concert halls combine these two types: most
of the audience seats are located at one side of the stage, while two
or three lines of seats revolve at the other three sides. These can be
used as chorus seats as well. Small concert halls normally chose the ended
stage. The choice of the performance watching style in large concert hall
is mainly influenced by the acoustic theory.
2) Interior design
The auditorium hall is the most important public space of the theater.
It is the best place to show the architect’s aesthetic taste and his design
talent. The design of architects always conflict with the acoustic design
and the technology requirements of the theater. The architect has to design
and coordinates thoroughly in order to keep his own interior design style,
while satisfying the function requirements of the auditorium hall.
The space of the auditorium hall is formed by the layout plan of the auditorium
hall, the seating floor appearance and the ceiling appearance.
For those theaters with frame stages, the space form of the auditorium
hall experiences three periods:
The traditional baroque style auditorium hall before the 2nd world war
is revolved by multi-floor compartments.
The functionism auditorium hall after the 2nd world war, which is based
on reasonable vision, rectangular shape, bell shape and fan shape, has
the grand suspended seating floor facing the stage.
Since the 1980s’, the revolved space of traditional auditorium hall has
been accepted again. The space of the auditorium hall returns towards
the traditional forms based on reasonable functions, expressing the traditional
revolving effect using modern design skills.
For theaters with open stages, no matter if classical theaters or modern
theaters, the effect of the revolving space is the aim they pursue. Only
the design skills of the modern theater are more flexible and changeable.
3) The design of the audience seating
The basic content of the audience seating design is to obtain good visual
effect for each audience, while satisfying the lowest restricted comfort
and safety.
For the arrangement of the audience seating, the comfort degree relies
on the distance between seating rows, the width and the design of the
seat itself. The safety degree relies on the width of the horizontal and
vertical corridors, the row amount of two horizontal corridors and the
seat amount of two vertical corridors, the width, the amount and the distribution
of the emergency doors, the gradient of steps and slopes, and the height
of railing, etc. <the design specification for the theater design>
has clear restriction for the lowest requirement. One thing worth noting
is that, the width of the horizontal corridor is not including the width
in front of the seats, which belong to the raw distance.
The standard for the good vision effect mainly includes three parts: the
sightlines, the vision distance and the vision range.
a. The Sightline
There are two parameters that should be defined first for sightline design:
one is the raising degree of the view line “c”, the other is the location
of the view point. When the raising degree of the view line is 12cm, it
will assure the audience can watch the viewpoint without any blocking.
The viewpoint is in the center of the curtain on the stage. Besides, that
there are other items to be noticed:
The level difference between the stage surface and the pit surface of
the first seating row affects the vision design a lot. The dimension must
be defined when starting the section design after the audience-seating
plan was arranged. Normally, the larger the volume of the theater, the
bigger the level difference.
The analysis of the sightlines not only includes the analysis of the sectional
sightlines, but also include the seating areas at both sides. For those
auditorium halls, which are seeking more popular revolving effect, the
analysis of the sightlines for the side seats should not be ignored.
The standard level of the sightlines in different audience seating area
should be treated differently according to the different seating classes.
This is the only way used in large theaters. To reduce the standard level
of the sightlines, one way is to raise or move the vision point backward.
Another way is to reduce the parameter “c”, or to arrange the seats raising
12cm every two rows, but it is difficult to maintain the unity and beauty
of the vertical corridor in this way, and the vision angle of the audience
is quite restricted. For other theaters such as children theaters, open
stage theaters, open theaters and nature sound theaters, the standard
level of the vision raising degree can be higher.
For the seating floor, especially the side seating floor, the railing
height at the front line should not block the sightlines. If it is too
low, then the thickness of the rail should be added in order to achieve
vision safety.
b. The vision distance
The design of the vision distance is mainly to control the longest distance
from the audience seat to the view point. It can be defined according
to different type of performance: not more than 30m in singing & dancing
performance, not more than 20m in drama & opera performance. The design
specification requires not more than 33m in singing & dancing performance
and not more than 28m in drama & opera performance (frame stage theaters);
due to the influence of the auditorium hall size, not more than 20m in
extended stage & central stage theater. There is no such specification
restriction in a concert hall; the function requirement can be looser
than the one of singing and dancing theater.
c. The vision range
In the design of the vision range, we have to control the biggest angles
of looking downward and looking horizontally. On the other hand the audience
in every seat can view the whole stage and more than half of the curtain
height.
4) The architectural acoustic effect
The acoustic specialist of the auditorium hall is in charge of the architectural
acoustic effect of the theater. Architects who can understand the basic
acoustic knowledge properly can help to keep the right design direction,
and solve the relative problems flexiblely during the design progress.
In the theaters using natural sound, the requirements for the acoustic
effects are different. The performance content varies from one to another.
The sound requirements have to be treated accordingly.
a. The opera & drama theater
The sound distinction of language is important in opera & drama performances,
so the mix-sound time should be lower, the volume of every seat which
affects the mix-sound time directly should be lower as well. As the strength
of the language sound is quite weak, the size of the auditorium hall is
consequently small.
b. The concert hall
In music performances, the music is the main sound; the tone and the harmony
are the basic aspects. Although it requires some clarity, the good mix-sound
degree, i.e. revolving feeling, warm feeling all sound characters are
required by a good concert hall. It requires bigger seating volume, longer
mix-sound time and stronger early side reflected sound. It requires bigger
volume of the concert hall and a smaller distance between sidewalls. The
early side reflected sound is getting more and more important in the acoustic
design in modern concert halls. The “grape garden” or “part of the shoe-box
shape” can be applied to reduce the distance between the vertical walls,
even for an auditorium hall with central stage. The size of these auditorium
halls can be larger, as the music and the singing sound are stronger than
the language sound.
c. The singing & dancing theater
The requirements for the sound character, the clarity, the mix-sound degree,
etc., is between the one of the opera & drama theater and the concert
hall. The mix-sound time and the seat unit volume are in between as well.
Different types of theaters have different sound requirements, To let
the audience seat get enough volume is the common aim, which every natural
sound dominated theater will pursue. Therefore we should add as much sidewalls
and ceiling reflected surfaces as possible, especially in the stage opening
and the orchestra pit area. These are the most important parts of the
reflected surface design. It is good for sound reflection to add more
side balconies.
We should avoid generating acoustic weaknesses in the shape design of
the auditorium hall. When designing walls, try to distribute the early
reflected sound well, scatter the mix-sound, and try to avoid sound focus
and echoes etc. In the seating floor design, the ratio of the floor height
and floor depth should not be less than 1:1.2.
If the theater is dominated by electronic sound, the acoustic design will
be as easy as the meeting room and cinema, which use sound-absorbing material
on the wall and ceiling to reduce the mix-sound time and to raise the
clarity. All sound effect is controlled by the electronic sound system.
5) The arrangement of the performance lighting, hi-fi, and
the control room
a. Lighting
The lighting in the auditorium hall includes the ear light, the face light
and the chasing light.
The ear light is distributed in the front half of the theater sidewalls.
The theater specification has clear requirement for the lighting angle
and the height to the stage surface. There is professional ear light room
in Mainland China theaters. It is not so common in western countries,
as they hang the ear light directly on the sidewalls or outside the balcony
of the side floor.
The face light is installed on the face light overhead-bridge of the ceiling
of the auditorium hall. The lighting angle should be between 45 and 50
degrees, the horizontal lighting width should not be less than the stage
opening width.
The chasing light can be installed on the chasing overhead-bridge of the
back ceiling or on two top ends of the back walls.
For the extended stage theater, the ear light and the face light must
be pointed to the far end of the stage according to their normal angle.
For the central stage theater, lighting should be installed around the
stage and on its top. The light around the stage is installed according
to the face light requirement, while chasing light should be installed
at several locations.
b. hi-fi
Although the architectural ways of adjusting acoustic effect is the main
method used in the natural sound dominated theaters, as electronic sound
system is installed in most of these theaters as backup, to be supplementary
and as amendment. The main speaker box of the auditorium hall is installed
on the speakers’ overhead-bridge on the top of the stage opening, or inside
the speakers columns at both sides of the stage opening. There are lots
of smaller speakers distributed on sidewalls, back walls, or in the ceiling
above and below the seating floor. The sound of these speakers should
be distributed well to all the audience.
c. Control room
For the frame stage theater, the control room for the lighting and hi-fi
should be arranged at back of the auditorium hall. People can view the
whole stage and the performance area from lighting control room; they
can hear the direct stage sound from hi-fi control room.
For the open stage theater, the lighting and hi-fi control room can be
planed either at the back of the auditorium hall or at two sides of the
stage, with the same requirement as the one for the frame stage theater.
The movable audience seating can be installed in the central pit area
of the auditorium hall. The control outlets and switches of lighting &
hi-fi can be left underneath and can be controlled by the director directly
during rehearsals. The location of the movable audience seating should
be defined by the size of the stage opening and the director’s habit location.
Considering the usage of the temporary visual and video recording control
system, the last row of the audience seats can be movable, with control
outlets left there.
3. The orchestra pit and the stage
There are mainly 2 kinds of stages, frame stage and open stage. The orchestra
pit usually is located between the frame stage and the auditorium hall
while the stage of the concert hall is usually open stage.
With regard to the components and dimension of a stage, mechanical specifications,
lighting, and the matters of curtain and background suspending system
of a stage, theater consultants should ask and integrate all the user’s
opinions and then make the technical designs as the bases of the civil
engineering design.
1) Frame stage
Frame stage, as the conventional stage type, is capable of creating vivid
scenes and illusion effects, and therefore, have been in use for very
long. Frame stage is comprised of stage opening, stage lip, master stage,
lateral stage, back stage, stage tower, and back warehouse, flexible scene
warehouse. Since most of the stage area is located behind the frame stage
opening, the space form of the stage mainly depends on the actual function
needs. If there is no space limitation, the master stage and subsidiary
stages all should be rectangular.
a. Stage opening
Stage opening is the frame of a frame stage and its dimension serves to
be a critical factor in the determination of the scale and dimension of
a stage, and is usually fixed according to the performance type, and the
scale of the auditorium. For the theaters that serve for troupes, the
opening dimension should be determined in accordance with the opening
dimensions of domestic theaters of the same level and scale.
b. Stage lip
Stage lip is the foremost part of a stage used for announcement, curtain
call and interval performance. The distance between the foremost part
edge of the stage lip and the curtain should not be less than 1.2 meters.
Foot light slots could be mounted outside the stage lip. At the ends of
a stage lip if there are stage ears, the width of the stage ear should
not be less than 1.2 meters and a door should be provided for performers
to get in and exit the stage.
c. Master stage
Master stage is main area for the performers to perform.
The width of the master stage should be determined according to the width
of the stage opening, and it is the width of the stage opening plus the
side curtains and the widths of the workspace of the two sides. The workspace
should not be less the width that machines above the stage tower, the
over bridge, and suspending cages occupy.
The depth of master stage is comprised of five areas, stage opening area;
performance area; scene area; velarium lighting area and velarium back
area. Stage opening area consists of 3 parts, which are fire prevention
curtain and water curtain sprinkle piping, all kinds of opening curtain
and false opening, and scrip curtain can be also placed in this area.
Performance area, scene area and velarium lighting area are divided by
side curtain and extended curtain into unit areas of the same width and
the width of each of the units is about 3 meters and could be determined
according to the need of the performance unit. The specifications of the
stage mechanical system and suspending system could be determined based
on those unit areas. Velarium back area connects the back over bridge
from the stage sides and its width should be wider than the over bridge.
The specification of the master stage machines varies upon different types
of theaters. Majority of singing and dancing theaters have the lift stage,
and majority of drama and opera theaters have revolving stage.
The fire prevention curtain should segregate master stage and auditorium.
False opening is a kind of frame equipment adjusting the size of the stage
opening. Its upper slide and side slide can move and the side facing the
stage can fix lighting on it.
d. Stage tower
The upper space of the master stage is stage tower used to hang soft scene
and lighting. Soft scene and lighting are fixed in the suspenders and,
the shafts of the soft scenes and lightings during performance and rehearsal
are realized by the lifting and lowering of those suspenders. Above the
stage tower is the tent ceiling. There are many layers of over bridges
on the lateral and back walls.
The tent ceiling is also called grape rack and grid ceiling, which serves
to be a workspace for the installation and maintenance of suspending system
and other equipments. For complicated and big suspending system, two layers
of grid ceiling should be built. The height of the lower part the grid
ceiling to the stage floor usually is 2.5 times of the height of the stage
opening, but at most should not be less than 2 times of the stage opening
height and plus 2 meters.
Over bridges are designed as working corridors for the installation, operation
and maintenance of the lighting system and suspending system above the
master stage and, usually appear to be 2-5 layers depending the scales
of the stage. The over bridges in the most upper part, which close to
the ceiling are used to place suspending system generators while some
of the larger theaters place them in a room outside the stage tower and
then those over bridges can be cancelled. The most lower over bridges
are located above the side stages and used for operating suspenders and
projecting lateral lighting. There should be some space left between the
most lower over bridges and the side stage ceiling for the HAV system.
The over bridges in the middle level are used for installing lighting
harbors, flying suspending equipment, arch velarium curtain installation
and equipment controlling. The back over bridges are used to connect the
over bridges from two sides.
e. Side stage
Side stage is located at the two sides of the master stage. If the space
is limited, there can be a one side stage or asymmetry stage. However
the entrance side should have a bigger side stage. The use of the side
stage is mainly for stage scene storage and change and, to keep all kinds
of vehicles and sets of performance for large theater.
The area of side stage should not be less than 1/3 of the master stage,
and its width should not be less the width of the stage opening. If there
are large vehicle stages used, its width should be larger than the length
of vehicle stage by 2 meters. The depth of the side stage should be 4/3
of the stage opening, and if there are large vehicle stages used, it should
be larger than the width of vehicle stage by 8 meters. The net height
of the lateral stage should be larger than the side stage opening between
the master stage and side stage, not including suspending system and general
used equipment system. The height of the side stage opening could be 1
meter less than the stage opening but should not less than 6 meters and,
its depth could be the same as the side stage. If there are large vehicle
stages used, it should be larger than the vehicle stages by 1 meter on
each side.
The upper space of the side stage could be used for suspending equipment
and maintenance over bridge.
Fire prevention and sound insulation curtain should be installed between
the side stage and master stage.
f. Back stage
Back stage is located in the back of a larger master stage, which connects
the side stages to form a frame shaped stage used for scene extension,
and vehicle stages, vehicle revolving stages and scenes. The upper space
of the back stage can also be used for suspending equipment, over bridges
and grid ceiling for maintenance.
The back of the lateral side of the back stage can serve as a place of
back projecting room which projects slides or movie to the velarium curtain
from back..
Fire prevention and sound insulation curtain should be installed between
the side stage and master stage.
g. Back warehouse
Back warehouse is used to accommodate the stage machineries. For vehicle
stages, thin revolving stages, and vehicle revolving stages, the mechanical
tunnel is not deep while the for the lift stages, cylinder revolving stages,
the machineries themselves occupy a larger space not mentioning that the
space needed for the in and out of the performers and scenes. Therefore,
the space of the back warehouse should be determined in accordance with
the stage machineries used.
2) The orchestra pit
The Orchestra pit is located between the frame stage and the auditorium
used for band and chorus accompaniment. Its dimension should be determined
according to the scale of the band. It is usually that the singing and
dancing theater requires a larger band while drama and opera theater small.
The average space per accompanist should be not less than 1 square meter
while the accompany singer should be not less than 0.25 square meters.
For the layout design of the orchestra, the length and width ratio should
not be high, and if it is over 3:1, then it is hard for the conductor
to control performance and the accompaniment shall be hard to be balance.
In terms of the elevation design of the orchestra, it can be divided into
open and semi open orchestra. Semi open orchestra can shorten the distance
between the performers and audience while the open orchestra provides
a better condition for the coordination of the conductor, accompanists
and performers on the stage, however there is one shortcoming which is
that the sound it produced may prevail the singing on the stage.
3) The open stage
Open stage is a kind of stage that does not have a frame stage opening,
the stage and the auditorium remain in the same space and it is mostly
used for drama, opera, musical and dance performances which do not require
imitational scene effect. The forms of the open stage are many and flexible
but could be categorized into three major kinds:
a. One end stage, the auditorium is located in one side of the stage and
the other three sides of the stage connect with the back stage.
b. Extension stage, the stage is surrounded by the auditorium by three
sides of the stage and one side of the stage connects with the back stage.
The shapes of the extension stage could be trapezoid, semi circular or
a polygon. Sometimes, extension stage connects with a frame stage as its
fore stage.
c. Central stage, the stage is surrounded by the auditorium by circle
and the shapes of the central stage could be square, circle and polygon.
The area of the open stage should be determined according the content
of the performance, stage technical requirement, and the scale of the
audience.
The stage machineries of the central stage include revolving stage and
lift stage. The revolving stage could be the cylinder type, shelf type
and thin revolving type and a larger back warehouse is required for the
previous types. Lift stage includes large lift stage and small lift block,
and many of small lift blocks combined together create a rich and versatile
stage space.
Except for music theater, all the open stages should install stage lighting
system and simple suspending system.
4 Back stage
It is critical to have a large back stage system to make the theater have
a good performance function. The system includes performer room, performance
facility room, and offices. The traffic of the system should separate
from the traffic of the audience and the VIP’s. Besides, the entrance
of the performers should separate from the scenes but can be the same
or separate one with the office-managing people.
1) Performer’s rooms
Performer’s rooms include cosmetic room, rehearsal room, water closet,
and rest room. During the performance, the activity space also includes
stage waiting area and stage running area. The net door height of performer’s
rooms and the height of corridors should not be less than 2.4 meters.
a. Cosmetic room
Cosmetic room can be divided into large, middle and small and the determination
of its number can refer to theater design code. The one person cosmetic
room provided for leading actors can be a suite, with the outside room
for meeting, practice and placement of a piano while the inside room be
used for make up and changing. A small sprinkle shower bath room can also
be provided. All the cosmetic rooms should provide sun blind system and,
artificial lighting similar to the stage should be provided for the makeup,
so do the hot and cold-water basins. All cosmetic rooms should provide
TV or broadcasting system that could show the stage status. Congregated
cleaning room and shower rooms should be provide in the cosmetic room’s
area and the rest room in this area can also be considered.
Cosmetic rooms should close to the stage, and it is better to be the same
level and close to the stage to shorten the distance to the stage. For
large-scale theaters, the cosmetic rooms can be designed to have two stories,
but no more than it. An elevator can also be considered.
The rest rooms for the band, conductors and the sound room should be adjacent
to the orchestra. The standard of the conductor’s rest room should be
the same as the single person cosmetic room.
b. Rehearsal room
Rehearsal room can be divided into large, middle and small ones.
The dimension of a large rehearsal room should be similar to the stage
with a net height not less than 6 meters and the upper lighting system.
For large and middle rehearsal rooms, a prolonged mirror no less than
2 meters in height on one side of the whole walls should be installed.
Wall skirt and rehearsal handrail should also be installed. Sound insulation
treatment should be taken and the flooring should be elastic. Men and
women’s change rooms should also be designed next to the rehearsal room.
The rehearsal room for chorus and band should be built with sidesteps
while small rooms can be used for solo practice with unparallel sidewalls
or better sound insulation treatment to prevent echo. The rehearsal rooms
should be far from the stage and have a good sound insulation effect.
c. Stage waiting area and stage runway
Stage waiting area is usually located in the stage entrance and exit (from
the auditorium facing the stage, the entrance is located on the left side
of the stage and the exit on the right side), and usually is wide corridor
or rooms for performers to wait. Emergency cosmetic room and small property
rooms can also serve as stage waiting area.
Stage runway is the passage, which connects the stage entrance and exit,
and therefore, it should be convenient. It could be designed outside the
stage back wall or outside the orchestra under the auditorium. Frame shaped
stage, which has a back stage, and larger scale theaters usually has the
latter one.
When stage-waiting area also serves as the stage runway, the width of
the passage should not be less than 2.8 meters.
2) Performance facility room
Performance facility includes soft scene, hard scene, property, costumes,
instrument, lighting and acoustic equipment and all of them (except the
instrument, lighting and acoustic equipment) require a processing space,
usage space and storage space. Therefore, convenient internal and external
transportation conditions are very important, and for the theater used
for troupes, the parking of the container vehicles and transportation
and storage of those containers inside theater could also be considered.
a. Processing space
Troupe resident theater should provide special spaces for metallic, wood,
electricity, costume and scene painting processing works in the theater.
If the space is limited, the processing spaces can be placed outside the
theater. The theaters used for itinerary troupes usually provide workshops,
maintenance rooms and art design rooms for multi purpose uses. However,
the scene loading and unloading platform and assemble workshop are necessities.
The processing and maintenance workshop should be located in the back
stage which is far from the stage while the loading and unloading platform
should be close to the side stage.
The criterion of the scene painting room is the strictest one. It not
only need a flooring or wall which could accommodate the whole soft scene,
but also need enough space to oversee it. The way of scene painting can
be divided to level lay painting and vertical hanging painting
b. Usage space
Performance facility usage space not only includes the stage, orchestra
and the auditorium, but also the costume and property rooms. Costume rooms
should set for men and women’s respectively, and ironing board and cleaning
basin should also be provided. Big property rooms should close to the
master stage and side stage while the small rooms should close to the
entrance and exit.
c. Storage space
Troupe resident frame stage theater can provide specialized spaces for
hard scene storage, soft scene storage, costume and property storage,
instrument storage, lighting equipment storage, and acoustic equipment.
For theaters mostly used for itinerary troupes, the storage spaces could
be simplified and diminished.
Specialized hard scene storage room usually is located in the side stage,
back stage or between of them. For large theaters with the lifting and
lowering systems, it could be located under the side back stage. The net
height of the hard scene storage room should be no less than 6 meters.
Soft scene storage room is the place for soft scene and usually located
in the back of the back stage. If there is no back stage, it can be located
in the back of the master stage for the convenient transportation and
storage from the suspenders. Soft scene storage space should be long rectangular
shelves, which parallel with the stage opening in its length, level with
the stage level on the top with a width larger than the soft scene and
a depth determined in accordance with the numbers of the shelf grid.
Instrument storage room should have several separate rooms of constant
temperature and humidity to store different instruments. Piano room should
have a larger passage from the stage.
Acoustic equipment room should pay attention to matters of moisture proof,
dust proof, magnetic proof and static electricity proof.
3) Offices
For troupe resident theater, its office space should satisfy all the need
of the managing staff and logistic staff of the whole troupe. For the
theaters mostly used for itinerary troupes, its office space should accommodate
theater managing staff, logistic staff and the troupe managing staff.
These two parts should be apart, the latter can be put together with actor/actress’
room
5. M & E rooms
The Mechanical & Electricity rooms of a theater can be divided into
general M & E system and specialized system
1) General M & E system
General M & E system refers the M & E system which satisfy the
equipment and electricity requirement of ordinary buildings, including:
a. AC system
b. Heating system
c. Fan system
d. Water supply system
e. Drainage system
f. Rain water system
g. Fire resistant water system
h. Switchboard system
i. General lighting system
j. Emergency lighting system
k. Fire prevention alarming system and controlling system
l. Building automatic control system
m. Security system
n. Office communication system
o. Public broadcasting system
p. Closed circuit television system
2) Specialized M& E system
Specialized M & E system refers to the system used for theater, including:
a. Stage mechanical M & E system
b. Stage suspending M & E system
c. Stage lighting system
d. Stage audio system
e. Stage monitor and communication system
f. Performance video recording and rebroadcast system
III Multi functional theater
Multi functional theater is a theater that can satisfy performances that
vary greatly. Its multi functionality mainly shows in the presence of
stage and auditorium and there are no great differences in other part.
Multi functional theater could be divided into frame stage multi functional
theater and open stage multi functional theater according to different
types of presentation.
1 Frame stage multi functional theater
Frame stage multi functional theater comes into emergence since that some
owners like their theaters satisfy different kind of performances. However,
the performance effect is hardly competitive with the specialized theaters.
The frame stage of the multi functional theater is based on the conventional
frame stage, its basic form of the stage and the auditorium remain the
same. For drama, singing & dance, and musical natural sound performances,
the major difference of their requirement to the theater is acoustic.
Therefore, by the installation of adjustable and mobile acoustic equipment
those performances could be satisfied.
1) The auditorium hall
In the auditorium, the ways used mostly to change the acoustic effect
includes, installation of equipment on the wall, which can change the
sound insulation features, such as sound insulation rollers and revolving
objects, etc; and lifting ceiling which can change the volume of the auditorium.
The two methods can be used the same time. However the latter one require
large scale machineries and a higher cost and is thus seldom used in the
country while the first method has multiple choices of lower cost and
thus used most often.
2) Stage
On the stage, mobile acoustic canopy is used separate the stage tower,
side stage and back stage from the master stage to satisfy different performance
needs.
Besides, the orchestra of multi functional theater is also ascendable
and descendible and serves as orchestra, auditorium and stage to adjust
the scale and function of the auditorium and stage. In the orchestra area,
it can also be restructured to be a extended stage or a semi circular
stage. If mobile chairs are place there, it can be part of the auditorium.
2 Open stage multi functional theater
Open stage multi functional theater is often used for different drama
and musical performance. Its concept varies a lot from the frame stage
multi functional theater. This kind of theater is commonly built and with
a high rate of usability, however its scale is normally small.
Black Box Experimental Theater is a very good example of a typical open
stage multi functional theater, which is normally rectangle in shape and
in small scale without fixed auditorium and stage. Its stage is usually
arranged to different shapes in accordance with the requirement of the
performance. To build to stage and auditorium, either manual work and
adoption of many units of small lift stages can be taken. In this kind
of theater, lighting and suspending system can be set up over the whole
theater to satisfy different layout requirement of different performances.
Black Box Experimental Theater took a eclectic way to solve the problem,
which is to set up a fixed auditorium and a fixed one end stage respectively
at the two ends of its rectangular space with a level space in the middle,
and by either manual work method or mechanical ways the theater arranges
different forms of stage.
For the open stage concert hall, by adjusting its acoustic equipment,
it could satisfy different performances from small scale solo to large
scale symphony. The acoustic equipment includes the lifting acoustic reflection
ceiling, acoustic rooms above the auditorium that can change the auditorium
volume, and the adjustable wall that adjusts the reflection effect.
IV Art Performance Center
As mentioned before, since there exist different type of performances
with different requirement there come to be the emergence of singing &
dancing theater, concert hall, drama & opera theater and multi functional
theater etc.. However, to require a better quality and to build performance
architecture which could represent their country, many of the owners combine
different theater together to from an architecture group. We refer this
architecture group to Art performance center.
The most common combination of a large scale comprehensive art performance
center is opera house, concert hall and drama & opera theater; large
scale symphony concert hall and small scale solo concert halls, and others
with a flexible small scales black box experimental theater.
The building combination of the art performance center can divided into
decentralized and centralized performance center. For the former one,
all its theaters possess independent and complete building and have its
own audience rest room, auditorium, stage and back stage facilities which
is favorable to stage by stage construction and independent management;
For the latter one, the theaters share audience rest rooms and back stage
facilities and it leave more public space to the theater inside and have
a efficient utilization of back stage facilities.
|